Spirals are curved lines that rotate around a centre and they move further away from it at each turn.
The separation between each turn is constant.
The separation between each turn increases in a certain way.
To look like the shape of the Archimedean spiral, the spirals can be constructed with two or more centres using a ruler and a compass. If a spiral has more centres, the separation between the turns will be closer to a constant value.
Some examples of spirals are:
Construct a spiral with two centres
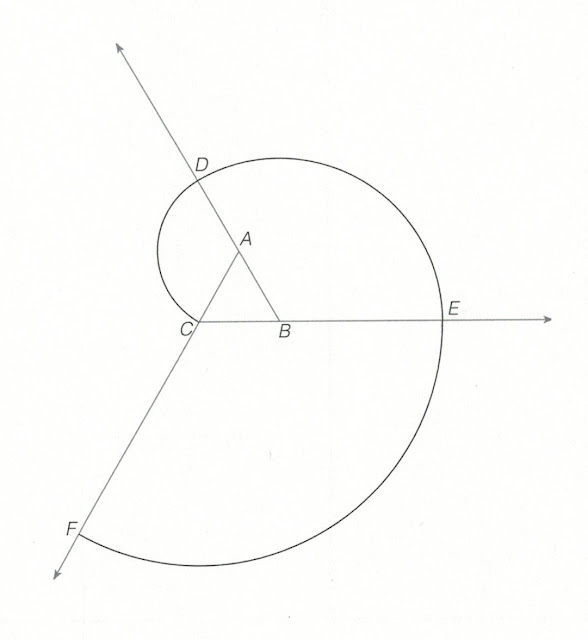
To construct a spiral given the two points A and B, follow these steps:
Step 1. Draw the segment AB.
Step 2. Use centre point A and radius AB. Draw half a circumference from B to C.
Step 3. Use centre point B and radius BC. Draw half a circumference from C to D.
Step 4. Use centre point A and radius AD. Draw half a circumference from D to E.
Step 5. Use centre point B and radius BE. Draw half a circumference from E to F, forming a spiral from the segment AB.
Construct a spiral with three centres
To construct a spiral with three centres, A, B and C, follow these steps:
Step 1. Draw an equilateral triangle ABC.
Step 2. Extend the sides of the triangle.
Step 3. Use centre point A and radius AC.
Draw an arc from C to D.
Step 4. Use centre point B and radius BD.
Draw an arc from D to E.
Step 5. Use centre point C and radius CE.
Draw an arc from E to F, forming a spiral with three centres.